Fire insurance is a key component of the general insurance sector, offering protection against loss or damage caused by fire and allied perils (like lightning, explosion, and implosion). As businesses, homeowners, and institutions prioritize risk management, the demand for fire insurance policies continues to rise.
Insurance agents remain pivotal in this space, advising clients, sourcing policies, and servicing claims. Their compensation is based on commission structures governed by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and influenced by industry competition. This article outlines the Fire Insurance agent commission chart 2026, regulatory developments, and key earning opportunities.
What Is Fire Insurance?
Table of Contents
Fire Insurance is a type of general insurance that provides financial protection against losses or damages caused by fire and related perils. It covers buildings, structures, machinery, stock, furniture, and other contents against fire-related incidents, helping individuals and businesses recover from unforeseen disasters.
What Does Fire Insurance Cover?
Fire insurance policies typically cover loss or damage caused by:
- Fire (accidental or due to external causes)
- Lightning
- Explosion/Implosion
- Impact Damage (e.g., from a vehicle or aircraft)
- Riot, Strike, Malicious Damage (RSMD)
- Storm, Tempest, Flood, and Inundation (STFI)
- Bursting or overflowing of water tanks or pipes
- Earthquake (if opted as an add-on)
- Terrorism (if opted as an add-on)
Types of Fire Insurance Policies:
- Standard Fire & Special Perils Policy (SFSP): Covers most fire and allied perils for residential, commercial, and industrial properties.
- Bharat Griha Raksha: A simplified fire insurance product for homeowners in India.
- Bharat Sookshma Udyam Suraksha: For small businesses with asset values up to ₹5 crore.
- Bharat Laghu Udyam Suraksha: For medium enterprises with assets between ₹5–50 crore.
Who Needs Fire Insurance?
- Homeowners (for property and contents)
- Shop owners
- Factories and warehouses
- Commercial establishments (hotels, schools, hospitals)
- Offices
- MSMEs and Corporates
Key Benefits of Fire Insurance:
- Risk Mitigation: Protects against large financial losses due to fire or related hazards.
- Peace of Mind: Ensures business continuity and home security.
- Loan Requirement: Often mandatory when taking a home or business loan.
- Flexible Coverage: Can be tailored with add-ons to cover specific risks like earthquakes or terrorism.
What Fire Insurance Does Not Cover:
- Fire due to willful negligence or arson
- War or nuclear risks
- Loss of earnings or business interruption (unless covered under a separate policy)
- Theft during or after a fire, unless specifically covered
- Spontaneous combustion, unless mentioned in the policy
Understanding Fire Insurance Policies:
Fire insurance can be purchased for:
- Residential buildings
- Commercial properties (shops, offices)
- Industrial properties (factories, warehouses)
- Institutions (schools, hospitals)
- Equipment and stock-in-trade
Fire insurance is usually offered under the Standard Fire and Special Perils (SFSP) policy or Bharat Sookshma Udyam Suraksha and Bharat Laghu Udyam Suraksha policies for MSMEs.
Regulatory Framework in 2026:
In 2023–2024, IRDAI shifted from product-specific commission caps to overall Expense of Management (EoM) guidelines, granting insurers flexibility in setting agent commissions. These changes continue into 2026.
Key IRDAI Directives (2026):
- No fixed commission limits per product (e.g., fire, motor, marine).
- Insurers are free to decide commission structures, provided overall EoM (as a percentage of gross written premium) stays within limits.
- Emphasis on promoting digital adoption, rural penetration, and MSME inclusion.
About Fire Insurance Agent:
A Fire Insurance Agent is a licensed individual or entity authorized to sell, promote, and service fire insurance policies on behalf of an insurance company. These agents play a key role in helping individuals, businesses, and institutions protect their property and assets against fire and related perils.
- Educates clients about the importance of fire insurance
- Assesses property risk and coverage needs
- Helps clients choose appropriate policies (e.g., SFSP, Bharat Griha Raksha)
- Facilitates policy purchase and documentation
- Assists in renewals and claims
Types of Fire Insurance Policies They Sell:
- Standard Fire & Special Perils Policy (SFSP)
- Bharat Griha Raksha (for homeowners)
- Bharat Sookshma Udyam Suraksha (for small businesses up to ₹5 crore)
- Bharat Laghu Udyam Suraksha (for MSMEs up to ₹50 crore)
- Custom fire policies for large corporations and industries
Role & Responsibilities:
- Client Assessment: Evaluate property type, value, and fire risk exposure
- Product Recommendation: Suggest the best policy type and add-ons (like earthquake or terrorism cover)
- Documentation: Assist with proposal forms, inspections, and declarations
- Policy Issuance: Help clients complete formalities and receive policy documents
- After-sales Support: Handle claims, renewals, endorsements, and grievance redressal
Eligibility to Become a Fire Insurance Agent:
- Minimum age: 18 years
- Education: 10th pass or higher
- Complete IRDAI-approved training (usually 25–50 hours)
- Pass the IRDAI licensing exam
- Get appointed by an insurer
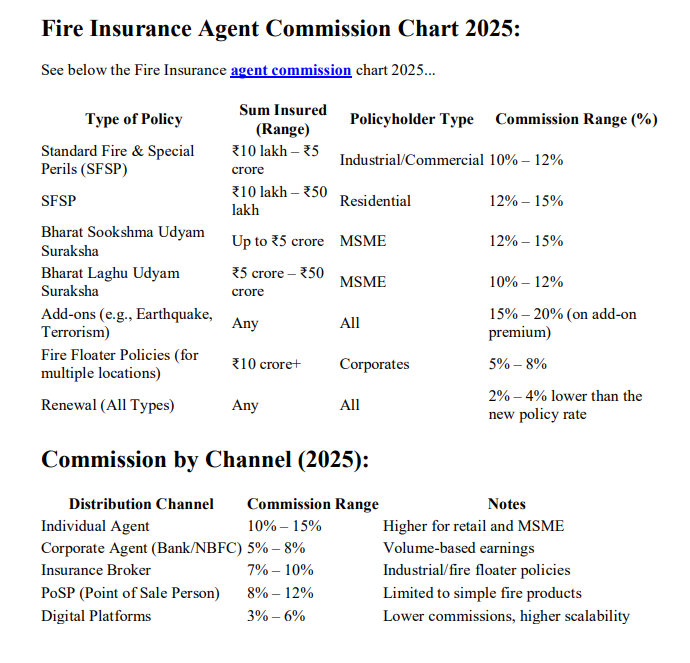
Fire Insurance Agent Commission Chart 2026:
See below the Fire Insurance agent commission chart 2026…
| Type of Policy | Sum Insured (Range) | Policyholder Type | Commission Range (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Fire & Special Perils (SFSP) | ₹10 lakh – ₹5 crore | Industrial/Commercial | 10% – 12% |
| SFSP | ₹10 lakh – ₹50 lakh | Residential | 12% – 15% |
| Bharat Sookshma Udyam Suraksha | Up to ₹5 crore | MSME | 12% – 15% |
| Bharat Laghu Udyam Suraksha | ₹5 crore – ₹50 crore | MSME | 10% – 12% |
| Add-ons (e.g., Earthquake, Terrorism) | Any | All | 15% – 20% (on add-on premium) |
| Fire Floater Policies (for multiple locations) | ₹10 crore+ | Corporates | 5% – 8% |
| Renewal (All Types) | Any | All | 2% – 4% lower than the new policy rate |
Commission by Channel (2026):
| Distribution Channel | Commission Range | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Agent | 10% – 15% | Higher for retail and MSME |
| Corporate Agent (Bank/NBFC) | 5% – 8% | Volume-based earnings |
| Insurance Broker | 7% – 10% | Industrial/fire floater policies |
| PoSP (Point of Sale Person) | 8% – 12% | Limited to simple fire products |
| Digital Platforms | 3% – 6% | Lower commissions, higher scalability |
See below the Fire Insurance Agent Commission Chart in PDF format.
Benefits of Being a Fire Insurance Agent:
- High commission potential on large-value property policies
- Stable and growing demand, especially from MSMEs and homeowners
- Long-term client relationships (annual renewals)
- Flexible working (full-time, part-time, or PoSP)
- Scope for cross-selling (e.g., burglary, liability, and business interruption covers)
Key Trends in Fire Insurance Distribution:
MSME Segment Focus: Government initiatives and IRDAI’s push for financial inclusion have expanded the MSME insurance base.
Increased Add-On Sales: Agents earn higher commissions on add-ons like earthquake, STFI (Storm, Tempest, Flood, Inundation), and terrorism.
Growth in Tier-II and Tier-III Markets: Fire insurance sales in rural and semi-urban areas offer new business potential for agents.
Bundled Insurance Packages: Fire coverage is often bundled with burglary, liability, and electronic equipment insurance.
Earning Potential of Agents in 2026
| Annual Premium Sourced | Avg. Commission (%) | Estimated Annual Income |
|---|---|---|
| ₹10 lakhs | 12% | ₹1.2 lakhs |
| ₹25 lakhs | 12% | ₹3 lakhs |
| ₹50 lakhs | 10% | ₹5 lakhs |
| ₹1 crore | 8% | ₹8 lakhs |
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Digital aggregators offering cheaper direct-to-consumer models
- Strict underwriting norms for fire insurance
- Need for detailed inspections and documentation
Opportunities
- Government mandates for fire insurance in certain sectors
- Cross-selling opportunities with property, liability, and burglary insurance
- Long-term policies (3–5 years) with upfront commissions
How Agents Can Maximize Earnings in 2026
- Focus on MSME clients for higher commissions and volume
- Upsell add-ons and value-added services
- Maintain a portfolio of renewals and new clients
- Leverage digital tools for policy issuance and CRM
- Build relationships with builders, developers, and industrial associations
Conclusion:
The Fire Insurance Agent Commission Chart 2026 reflects a more dynamic and performance-oriented structure, where agents have the flexibility to earn based on effort, specialization, and strategic focus. With regulatory reforms supporting innovation and expansion, agents who embrace digital tools, understand client needs, and offer complete risk solutions stand to benefit the most in this evolving landscape.
FAQ
Q. Who is a Fire Insurance Agent?
A. A fire insurance agent is a licensed individual or corporate entity authorized by an insurance company to sell, promote, and manage fire insurance policies for individuals, businesses, and institutions.
Q. How is commission paid to agents?
A. Commission is usually paid on every policy sold, either monthly or quarterly, depending on the insurer’s payment cycle. It’s calculated as a percentage of the premium (excluding GST).
Q. Can fire insurance agents earn performance-based incentives?
A. Yes. Many insurers offer additional incentives for high-performing agents, such as:
- Cash bonuses
- Slab-based commission hikes
- Domestic and international travel rewards
- Recognition awards
Q. Can a fire insurance agent work with multiple insurers?
A. Only insurance brokers and composite/corporate agents can represent multiple insurers. An individual agent is typically tied to one insurer unless licensed as a Point-of-Sale Person (PoSP) or broker.
Q. Is prior experience required to become an agent?
A. No. Anyone who meets the basic eligibility requirements and passes the required exam can become an agent. Insurers often provide product training to new agents.
Q. Do agents assist in claim settlement?
A. Yes. A good fire insurance agent guides clients during the claim process, helping with documentation, inspection coordination, and communication with the insurer.
Q. Is fire insurance commission better than motor insurance?
A. Yes and no. Fire insurance commissions are higher per policy due to large sum insured values (especially in commercial cases). However, motor insurance has higher volume and faster sales cycles. Many agents sell both for a balanced portfolio.